Published : August 28, 2017

Capital market structure of India is complex. Also, it makes up the significant part of a financial market. Let us look at the basic definition of the Capital Market. It is a place for long-term financial assets which have long or indefinite maturity. The capital market provides long-term debt and equity finance for the government and the corporate sector.
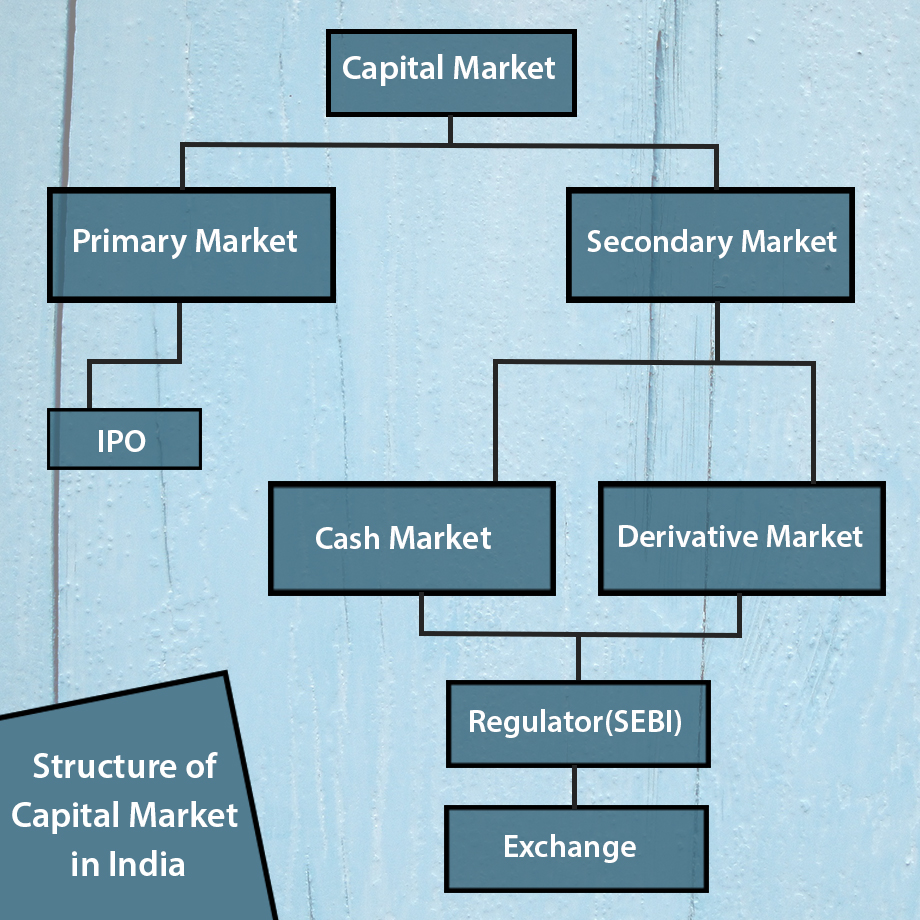
Secondary Market has got two wings namely Cash Market and Derivative Market.
SEBI (Securities and Exchange Board of India) is a regulator of Indian Capital Market. It was established in 1988. The basic function of SEBI is to protect the interest of investors.
SEBI is also the Regulator for Commodity Market. Prior to this Forward Market Commission (FMC) was the regulator of the commodity market.
Exchange provides an electronic and transparent platform to buy and sell the shares. Stock exchange also provides the facility for issue and redemption of securities.
In India, there is two national Exchange of stock market. They are the NES and the BSE. Further, there are two national exchanges for commodity, MCX & NCDEX.
The history of Exchanges of Indian Capital Market is way back to the 1800s. The following are the milestones in the Indian capital market
The 1800s
The 1900s
The 2000s
The broker acts as a bridge between the exchange and traders (Buyers & Sellers). Moreover, any Indian can invest or trade in a stock market or commodity market. But for this, you have the open Demat account with a registered broker.

Enjoy flexible trading limits at
lowest brokerage rates ?
Open Your Investments Account Now
0Account Opening Charges
Life Time Demat AMC
Brokerage








IT'S TIME TO HAVE SOME FUN!
Your family deserves this time more than we do.
Share happiness with your family today & come back soon. We will be right here.
Investment to ek bahana hai,
humein to khushiyon ko badhana hai.
E-mail
askus@rmoneyindia.com
Customer Care
+91-9568654321